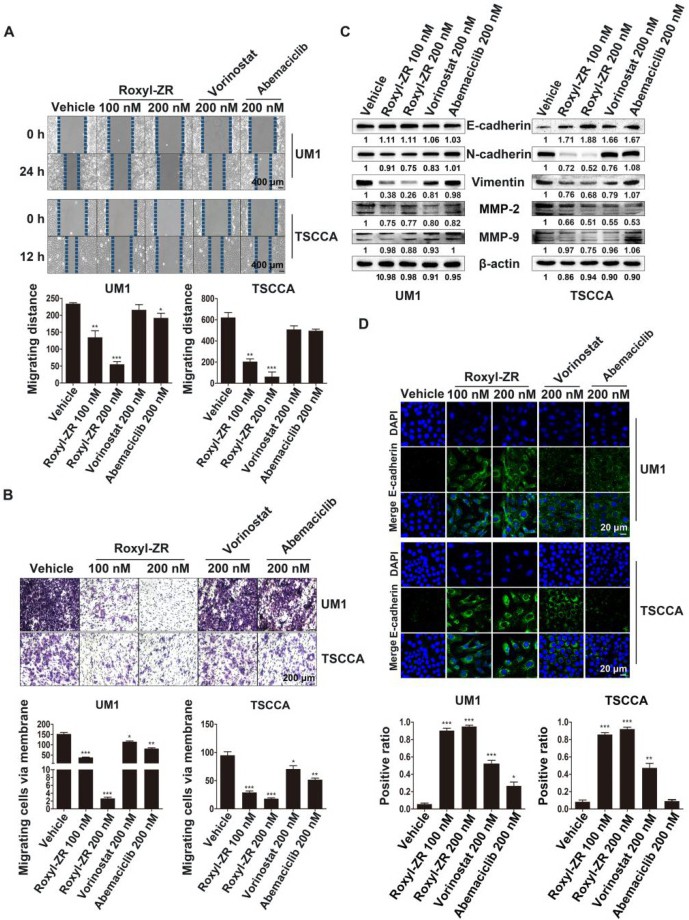
Fig. 3. Roxyl-ZR inhibits migration and invasion of OSCC cells. (A) Roxyl-ZR delayed scratch healing in UM1 and TSCCA cells (compared with other groups, as determined by a wound healing assay). (B) Roxyl-ZR effectively decreased the invasion of UM1 and TSCCA cells compared with the other groups, as determined by Transwell assay. (C) Cells were treated with Roxyl-ZR, vorinostat, abemaciclib, or vehicle for 48 h. Roxyl-ZR significantly up-regulated E-cadherin abundance and down-regulated N-cadherin, vimentin, MMP-2, and MMP-9 abundance with anti-β-actin as a loading control, as determined by western blot assay. (D) Roxyl-ZR significantly induced E-cadherin expression compared with other groups, as determined by immunofluorescence assay. E-cadherin in green was stained by Alexa-488 and cell nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue).